What is media filtration?
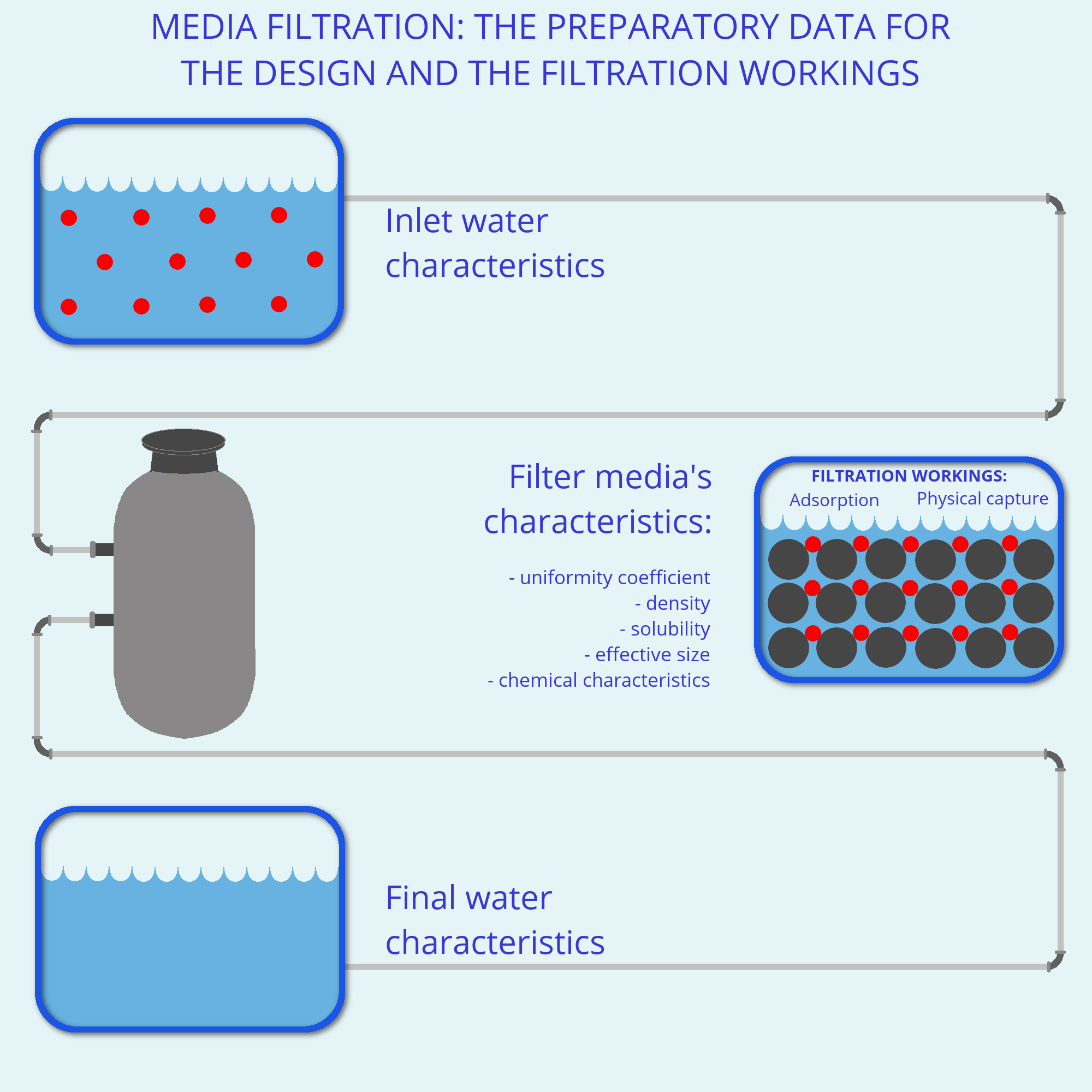
Media filtration functions by two workings: the first is the
physical capture of the components and the second is the adsorption.
In the first mechanism the inlet water flux passes through the filter media and the pollutants remain trapped in the empty spaces between particles and in the filter media's particles surface. In the second pollutants' molecules are fixed in the filter media surface because of a physical or chemical interaction.
Characteristics
Filtration systems are typically composed by sand, organic matter, activated carbons or other materials. Often media filters are not composed by one material, but there are different layers of different materials and in that case they are defined as multi media filters.
The choice of the filter media to use, alone or in combination with others, depends on which are the components to remove and the following chemical and physical filter media characteristics must be considered:
- the uniformity coefficient, the ratio between the dimension of the sieve holes which restrain 40% (dry weight) of the filter medium and the dimension of the sieve holes which restrain the 90% of the filter medium. It represents the heterogeneity of the dimensions of the filter media particles;
- the effective size or effective diameter, the dimension of the sieve holes which restrain the 90% in weight of the filter media;
- the density;
- the solubility.
Medium filter can be based on gravity or on pressure, depending on the total components contained in the solution, on the filter medium granulometry and on the final result to achieve.
A coagulant, a polyelectrolyte that increases process' efficiency enlarging particles to remove, it can be added to the media filtration system. Sometimes flocculation and upstream sedimentation are necessary.
A media filter can treat a certain water amount before a reclassification of the masses it's necessary to clean it from the retained solids. The cleaning process consists in a washing with clean water, and sometimes also with air, in the opposite direction to the filtration one, called backwashing.
Applications
Media filtration can be applied as a pre - treatment or a post – treatment in other water treatment systems, or it can be used as a stand alone system. The most common applications of the media filtration are:
clarification, sediment and suspended matter decrease/removal;
- chlorine (Cl) decrease/removal;
- water colour and smell decrease/removal;
- iron (Fe) decrease/removal;
- manganese (Mn) decrease/removal;
- hydrogen sulphide (H2S) decrease/removal;
- arsenic (As) decrease/removal;
- acid neutralization;
- sulphur (S) decrease;
- pre-treatment and post-filtration serving membrane filtration.
Our wide experience allows us to advice the customer on which kind of filter media can be more efficient for the resolution of the problem among the existing ones.
Kinds of filter media

Activated carbons
Activated carbons are composed by different kind of materials depending on their applications. The bituminous minerals and the coconut are the most common kinds used for water treatment.
The terms activated refers to the activation process that the carbon undergoes and that gives it a great porosity and a consequent adsorption surface increasing. Activated carbons have specific properties depending on the original material and the activation mode. Activated carbons can be used alone or in combination with sand. They are particularly suitable to remove acids, oxidation products, sulphates, chlorine, ozone, permanganate, and components which cause unpleasant smell and taste and all the organic molecules which contribute to form trihalomethanes. Activated carbons need to be periodically regenerated and it must be considered that, during the filtration and the backwashing, a part of the filter material is damaged.

Anthracite
The anthracite has an irregular form, which allows to form intergranular spaces, where components can deposit. Those spaces ensure also a minimal pressure loss and a good flux velocity.
The anthracite is often used alone, or in overlaid layers with different granulometry, or in combination with sand to form dual media filter. In those filters anthracite is the superficial layer that store a big volume of solids, extending the filter material life period. The sand layer below is a fine filter for the solids which cross the anthracite.

Sand
The sand made of quartz, or quartzite, is often used to remove suspended solids, as sand, silt or other inerts, and iron in its oxidized form, which contribute to the water turbidity. In the presence of colloidal substances sand can be an efficient filtration method if in the inlet water flocculants and coagulants are added .
Quartzite is cheaper than other filter materials, but it must be replaced very often. This is due to the fact that during the filtration the sand finer particles remain in the filter media surface layer, while the bigger ones are deposited on the bottom. Consequently the filtering capability decreases because all the particles can be filtered only by the fine surface filter media layer, where particles has the minimum space between each others. To solve this problem, sand is often used in combination with other filter media, with different density, above all the anthracite. A sand filter can remove components with dimensions up to 25-50 micron, but also finer, decreasing the velocity of the bed crossing or over - sizing the filter. The sand filter is mainly used for the primary treatment of waters for civil and industrial use, the pre - treatment for ion exchange and reverse osmosis plants and the refining of the mixed water from clariflocculation plants.
Pyrolusite
The pyrolusite is a mineral constituted by manganese dioxide. It is mainly used to remove iron, manganese and small quantities of sulphuric acid. Iron and manganese are adsorbed by filter media, they pass in their oxidised form and they precipitate, remaining captured in the media interstitial spaces. The manganese oxidation is more difficult than the iron one, if manganese doesn't pass in its solid form all adsorbing sites remain occupied and the soluble manganese passes the filter. For this reason, upstream of the filter, oxidants, as chlorine, potassium permanganate or ozone, are added to help manganese to pass into its oxidised form, making free all adsorbing sites with the best possible efficiency.
Ferric hydroxide
Because of its great chemical reactivity, ferric hydroxide is used for the adsorption of arsenic (in both its chemical forms, III and IV) and others heavy metals, as selenium, copper, vanadium, lead, antimony, molibdenum and phosphate. Ferric hydroxide removes selectively the arsenic (or the other chemical substances above) from the solution by adsorption. The chemical compound precipitates and it can be removed by filtration. This is the most effective method to remove arsenic from water, however some parameters, as pH and temperature must be controlled, because they influence iron oxidation. High concentrations of organic matter, orthophosphate or silicate decrease the percentage of removed arsenic because they compete with it for the absorption sites of ferric hydroxide.
Multimedia filter
In multimedia filter, materials with different density are used. The surface layer is usually formed by anthracite, the central layer is constituted of silica sand and the bottom layer is made by high density material, generally defined as garnet. This one can be constituted for example of aluminium silicate. The biggest particles are the anthracite's ones, the sand's particles are a medium size, while garnet's ones are the finest. The described materials are the most used because they have significant differences in their density and in this way the densest layer forms a block for the sand layer, just like this one represents a block for the anthracite layer. The stratification makes big dimension contaminants to be captured in the first surface layer, while particles with smaller dimensions move in the layers below. In this way a more efficient turbidity removal is grantee and the media needs less frequent washing. The materials arrangement in the multimedia filter has the aim to combing all the media's strengths in a single filter: the long time life of the filter media of big size and the great filtration capacity of the finer filter media. A multimedia filter can remove components with dimensions up to 10-25 micron.
Our plant
Installation place: Pontedera (PI)
Plant flow rate: 35 mc/h
Problem to solve: the necessity to have a plant that makes the water's characteristics to remain in the parameters values provided by D.Lgs. 31 of 02/02/2001.
Kind of plant: an iron and manganese removing plant with a pyrolusite bed with the injection of sodium hypochlorite by proportional and automatic dosing groups, to decrease ammonium and bacteria. This plant is equipped with a washing and back washing system, commanded by the pneumatic valves, ordered by a PLC programmed by us, which carries out the operations in a automatic way. A reverse osmosis plant to decrease chlorides concentration is also installed.
Our customers
PPM offers its services to:
- mechanic industry;
- chemical industry;
- paper industry;
- ceramic industry;
- pharmaceutical and cosmetic industry;
- galvanic industry;
- wood industry;
- leather and textile industry;
- petrochemical industry;
- plastic industry;
- agro – food industry;
- painting and graphic industry;
- car wash;
- Petrol stations;
- Urban waste water treatment for integrated water services, public authorities and large or tourist establishment.
How do we work?
In the first work phase PPM's experienced staff studies the customer's request to collect necessary data for the planning. Usually it's necessary to realize the inlet water's chemical – physical analysis and a visit can be useful. During this phase the preparatory data for the real designing are evaluated: the inlet water characteristics and the customer's needs, as water properties, the flow rate, the costs-benefits analysis and the maintenance process.
The next phase is the plant designing, in the case of the media filtration which filter media is the most suitable to solve the problem it's evaluated . All the plant's technical characteristics , the hydraulic and electric scheme and the components' arrangement are defined. Then the plant is realized by the assembly of the structure and all the components, always ensuring the best materials' quality. The plant is installed and tested at its final position.

